optical activity polarimeter definition|enantiomer optical activity : solution Theory: Acetanilide is prepared from aniline when it reacts with acetic . 2 de fev. de 2024 · O site bets.io é seguro? Esse site possui selo de segurança https ou SSL, registrado pela empresa Google Trust Services LLC, com validade até 26/3/2024. .
{plog:ftitle_list}
21 de dez. de 2023 · Bantubet Moçambique. Viva a emoção dos jogos Virtuais na plataforma Bantubet Moçambique. Junte-se à diversão hoje mesmo.
Optical activity is the ability of a compound to rotate the plane of polarized light. This property arises from an interaction of the electromagnetic radiation of polarized light with the unsymmetric electric fields generated by the electrons in a chiral molecule.Theory: Acetanilide is prepared from aniline when it reacts with acetic .
what is a polarimeter
Optical activity is measured by a polarimeter, and is dependent on several factors: concentration of the sample, temperature, length of the .
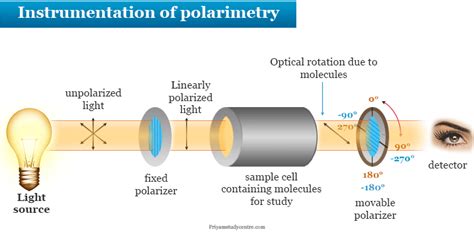
Polarimeter is the instrument that measures the direction and angles of rotation of plane-polarized light. The plane-polarized light pass through the sample tube containing the solution of sample, and the angle of .The instrument used to measure optical activity is called a polarimeter. A polarimeter is an instrument that allows polarized light to travel through a sample tube containing an organic .A polarimeter is a scientific instrument used to measure optical rotation: the angle of rotation caused by passing linearly polarized light through an optically active substance. Some chemical substances are optically active, and linearly polarized (uni-directional) light will rotate either to the left (counter-clockwise) or right (clockw.
A polarimeter is an instrument used to determine the angle through which plane-polarized light has been rotated by a given sample. You will have the opportunity to use a polarimeter in the . What is optical rotation? What is optical activity? What is the formula for specific rotation? What is (+) vs (–), d vs. l, D vs L, and R vs S? And more!The angle of rotation can be measured with an instrument called a polarimeter, represented in Figure 5.6. A solution of optically active organic molecules is placed in a sample tube, plane .A polarimeter is an optical instrument for accurately measuring the angle by which the polarization direction of light is rotated in an optically active medium.
A polarimeter is an optical instrument with which one can accurately measure the angle by which the polarization of light is rotated e.g. when it passes through an optically active medium (containing chiral molecules).. Operation Principle .Study Notes. A polarizer is a device through which only light waves oscillating in a single plane may pass. A polarimeter is an instrument used to determine the angle through which plane-polarized light has been rotated by a given sample. .
Study Notes. A polarizer is a device through which only light waves oscillating in a single plane may pass. A polarimeter is an instrument used to determine the angle through which plane-polarized light has been rotated by a given sample. You will have the opportunity to use a polarimeter in the laboratory component of the course. An analyzer is the component of a .Optical Activity. Optical activity of an organic compound refers to the property of an organic compound by the virtue of which, it rotates the plane polarised light (produced by passing ordinary light through Nicol prism) when it is passed through their solutions and the compounds are known as optically active compounds.. The optical activity of the substance is a measure of the .Optical activity is a macroscopic property of a collection of these molecules that arises from the way they interact with light. Compounds, such as CHFClBr, that contain a single stereocenter are the simplest to understand. . The instrument with which optically active compounds are studied is a polarimeter, shown in the figure below.Optical Activity Practice Problems Problem 1. What is optical activity, and how does it relate to chiral compounds? Provide an example of a chiral molecule. Problem 2. Calculate the specific rotation of a compound if a 1 cm thick sample solution in a polarimeter turns the plane-polarized light by 25 degrees and the concentration of the compound .
When optical rotations are expressed in this standard way, the specific rotation, [α] D, is a physical constant characteristic of a given optically active compound.For example, (+)-lactic acid has [α] D = +3.82, and (−)-lactic acid has [α] D = −3.82.That is, the two enantiomers rotate plane-polarized light to exactly the same extent but in opposite directions.Polarimetry definition & applications for AUTOPOL automatic Polarimeters. Biots law, chemical, food, flavor, and pharmaceutical industries. . nondestructive technique for measuring the optical activity exhibited by inorganic and organic compounds. . 546, 436, 405, and 365nm in a photoelectric polarimeter, have been found to provide .
Optical activity is a property unique to chiral substances. For example 2-butanol, which possess a chiral center (one carbon bound to four different ligands). Figure 1 illustrates that 2-butanol exists as two mirror-image isomers, or enantiomers .
Ask the Chatbot a Question Ask the Chatbot a Question optical activity, the ability of a substance to rotate the plane of polarization of a beam of light that is passed through it. (In plane-polarized light, the vibrations of the electric field are confined to a single plane.) The intensity of optical activity is expressed in terms of a quantity, called specific rotation, defined by an .Definition of polarimetry. Polarimetry is a superior, sensitive and nondestructive measuring technique for the measurement of optical activity, as exhibited by inorganic as well as organic compounds. . The measured value in a polarimeter is the optical rotation, α [°OR]. From the optical rotation further values can be derived:Definition. A polarimeter is an instrument used to measure the optical activity of a substance, which is the ability of a material to rotate the plane of polarized light. . The optical activity measured by a polarimeter can be influenced by several factors, including the concentration of the optically active substance, the path length of the .
Definition. Optical activity is the ability of certain substances to rotate the plane of polarization of light passing through them. This phenomenon occurs due to the chiral nature of the molecules in these substances, meaning they lack symmetry and can interact with light in unique ways. . Optical activity is measured using a polarimeter .The phenomenon of optical activity was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot in 1815. 2.6.2 Polarimeter. The instrument used to measure optical activity is called a polarimeter. A polarimeter is an instrument that allows polarized light to travel through a sample tube containing an organic compound and the degree to which an organic compound rotates .
polarometer optical activity
Optical activity is the ability of a substance to cause optical rotation or circular dichroism: Optical rotation is the phenomenon that the polarization direction of light is gradually rotated clockwise (dextrorotary) or anti-clockwise (levorotary) .If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
Synthetic aperture radar image of Death Valley colored using polarimetry.. Polarimetry is the measurement and interpretation of the polarization of transverse waves, most notably electromagnetic waves, such as radio or light .Definition of polarimetry. Polarimetry is a superior, sensitive and nondestructive measuring technique for the measurement of optical activity, as exhibited by inorganic as well as organic compounds. . The measured value in a polarimeter is the optical rotation, α [°OR]. From the optical rotation further values can be derived:
This notation means that the measurement was conducted at 25 o C using the D-line of the sodium lamp (λ=589.3 nm). A sample containing 1.00 g/mL of the compound in a 1 dm tube exhibits an optical rotation of 3.5 o in clockwise direction. Note that the instrument used in Chem 30BL and Chem 30CL can provide the specific optical rotation, which already corrects the .Optical Activity Laboratory Organic Chemistry Lab: AEMoody This laboratory will introduce you to basic principles of optical activity and the use of a simple polarimeter; for example, the relationship of the specific rotation, [α], of a molecule to its concentration, c (units: g/mL), in solution and the pathlength, l (units: dm), of the .
The angle of rotation can be measured with an instrument called a polarimeter, represented in Figure 5.6. A solution of optically active organic molecules is placed in a sample tube, plane-polarized light is passed through the tube, and rotation of the polarization plane occurs. The light then goes through a second polarizer called the analyzer. Optical isomerism. Optical isomers are named like this because of their effect on plane polarized light. Simple substances which show optical isomerism exist as two isomers known as enantiomers. A solution of one enantiomer rotates the plane of polarisation in a clockwise direction. This enantiomer is known as the (+) form.Definition of polarimetry. Polarimetry is a superior, sensitive and nondestructive measuring technique for the measurement of optical activity, as exhibited by inorganic as well as organic compounds. . The measured value in a polarimeter is the optical rotation, α [°OR]. From the optical rotation further values can be derived:Optical activity is the ability of a substance to rotate the plane of polarization of light passing through it. This phenomenon occurs due to the asymmetric arrangement of atoms within certain molecules, which interacts differently with left- and right-handed polarized light. Optical activity is crucial for understanding the behavior of light in various contexts, especially in the interaction .
polarity and optical activity
bulk Thickness Measurement
Exercise 3.14. The specific rotation of (R)-limonene is +11.5 o in ethanol.What is the expected observed rotation of a sample of 6.00 g (S)-limonene dissolved in ethanol to a total volume of 80.0 mL in a 1.00 dm (10.0 cm) pathlength cuvette?Exercise 3.15. The specific rotation of (S)-carvone is +61 °, measured 'neat' (pure liquid sample, no solvent).The optical rotation .
Optical rotation (OR) polarimeters measure only the OR of a linearly polarized wave vector caused by the optical activity of the measured material. Such polarimeters are used to detect optically active materials and measure their concentration. Here we describe a novel type of high-resolution OR polarimeter. The new polarimeter is a compact device, based on a .Anisotropic crystalline solids, and samples containing an excess of one enantiomer of a chiral molecule, can rotate the orientation of plane-polarized light. Such substances are said to have optical activity.Measurement of this change in polarization orientation is called polarimetry, and the measuring instrument is called a polarimeter.These measurements are useful for studying .
OEM Thickness Measurement
ODM Thickness Measurement
webSaiba como se inscrever, escolher acomodações, pagar e cancelar sua reserva no Sesc Bertioga. Veja também outras formas de visitar o centro de ferias.
optical activity polarimeter definition|enantiomer optical activity